International Commercial Terms
Introduction
In the complex world of global trade, purchase and sale agreements between countries are very common. To avoid ambiguity and disputes in these contracts, a set of standardized rules and terms known as Incoterms has been established. Incoterms, as a common language in international trade, specifies the duties, responsibilities, and costs of the parties involved in the transaction. This article will provide a comprehensive review of Incoterms, their types, importance, and applications in international trade.
What are Incoterms?
Incoterms is short for International Commercial Terms, which translates to “اصطلاحات تجاری بینالمللی” in Persian. This set of rules is formulated by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) and is periodically updated. The primary aim of Incoterms is to create a common language between the seller and buyer in international trade agreements to prevent disputes arising from different interpretations of contract terms.
Importance of Incoterms
- Determining Responsibilities: Incoterms clearly define who is responsible for transportation, insurance, customs, costs, and risks associated with the goods.
- Reducing Disputes: By using Incoterms, many disputes arising from different interpretations of contract terms are minimized.
- Facilitating Trade: Incoterms serve as a common language that simplifies international trade processes.
- Increasing Assurance: The use of Incoterms ensures that the rights and obligations of the parties are clearly defined.
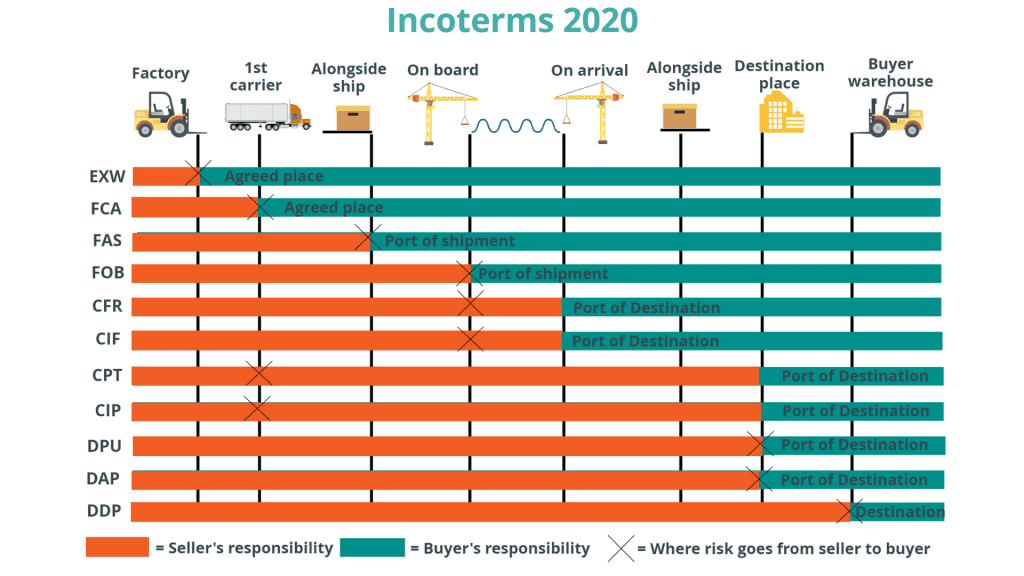
Categories of Incoterms
Incoterms are divided into four main groups:
- Group E (Ex Works): In this group, the seller delivers the goods at their premises, and all costs and risks from that point onward are the responsibility of the buyer.
- Group F (Free Carrier): In this group, the seller delivers the goods to a carrier and pays for the costs up to that point. Subsequent costs and risks are the buyer’s responsibility.
- Group C (Cost and Freight or Carriage and Insurance Paid to): In this group, the seller covers the costs of transportation and may also pay for insurance.
- Group D (Delivered): In this group, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the specified destination.
Important Terms in Incoterms
- FCA (Free Carrier): The seller delivers the goods to the carrier.
- FAS (Free Alongside Ship): The seller delivers the goods alongside the ship at the port of departure.
- FOB (Free on Board): The seller delivers the goods on board the ship at the port of departure.
- CFR (Cost and Freight): The seller pays for transportation costs to the port of destination.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight): The seller covers the cost of transportation and insurance to the port of destination.
- CPT (Carriage Paid To): The seller pays for transportation to the specified destination.
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid to): The seller covers the cost of transportation and insurance to the specified destination.
- DAF (Delivered at Frontier): The goods are delivered at the specified border.
- DES (Delivered Ex Ship): The goods are delivered on board the ship at the port of destination.
- DEQ (Delivered Ex Quay): The goods are delivered at the quay at the port of destination.
- DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid): The goods are delivered at the destination, but customs duties are the buyer’s responsibility.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): The goods are delivered at the destination with all costs, including customs duties, borne by the seller.
Importance of Correct Incoterm Selection
Selecting the correct Incoterm in international trade contracts is crucial because it impacts:
- Determining the Price of Goods: Transportation, insurance, and customs costs affect the final price of goods.
- Determining Responsibilities: Each Incoterm defines different responsibilities for the seller and buyer.
- Reducing Risks: Proper Incoterm selection can mitigate risks related to transportation and customs.
Facilitating Dispute Resolution: In case of disputes, Incoterms serve as a legal reference.
Conclusion
As a powerful tool in international trade, Incoterms help companies draft their commercial contracts transparently and accurately. Familiarity with Incoterms and selecting the correct one play a significant role in the success of international transactions.
Recommendations
- Consult a Specialist: To select the correct Incoterm, it is advisable to consult a legal or trade advisor.
- Thoroughly Review Contracts: Before signing a contract, carefully review all terms and ensure a correct understanding of the Incoterms used.
- Keep Information Updated: Incoterms are periodically updated, so always use the most recent version.

 then 'Add to home screen'
then 'Add to home screen' then 'Add to home screen'
then 'Add to home screen'



بدون دیدگاه